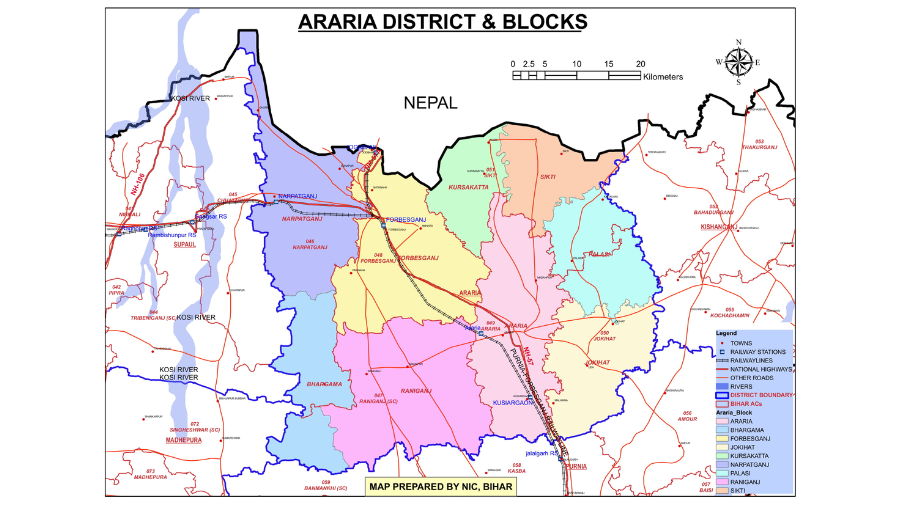
Araria is a district located in the northeastern part of Bihar, India. It is bordered by Nepal in the north, Kishanganj in the east, and Supaul in the west.
Araria has a rich history dating back to ancient times when it was ruled by the Kiratas, Pundras, and Angas. During the Mauryan period, it formed part of the Mauryan Empire. In the 6th century A.D., the area was under the Gupta kings Budhgupta and Devagupta, who gave Koti-Varsha for the maintenance of the Varaha Kshetra pilgrim center.
The district also witnessed skirmishes during the first war of independence in 1857. Araria became a full-fledged district on January 14, 1990, after the division of Purnia into three districts.
Contents
- 1 District Administration
- 2 Area & Population
- 3 Industrial Profile
- 4 Infrastructure
- 5 Heritage & Tourism
- 6 Geography & Climate
- 7 Economy & Industries
- 8 Culture & Places of Interest
- 9 FAQs
- 9.1 How many blocks are in the Araria district?
- 9.2 What is the primary occupation in Araria District?
- 9.3 Which key industries operate in Araria, and why are they significant?
- 9.4 What are the major crops grown in Araria District?
- 9.5 How is the transportation network in Araria District?
- 9.6 What facilities are available in Araria for healthcare and education?
District Administration
The district headquarters is located in Araria town. Araria district comprises two sub-divisions, which have been divided into nine blocks: Araria, Bhargama, Forbesganj, Sikti, Raniganj, Jokihat, Kursakanta, Narpatganj, and Palasi. The district has a total of 218 Panchayats and 742 villages.
Araria district is primarily agricultural, with paddy, maize, and jute being the major agricultural products. There are also many jute mills in Araria. The district has been developing its IT culture since 2002 with the establishment of the NIC District Center.
Area & Population
The total area of the Araria district is 2830 hectares, with a population of 28,11,569, according to the latest census. The population density is 993 per sq km, and the population growth is 30%. The sex ratio is 921 per 1000 males, and the literacy rate is 53%. The languages spoken in the district are Hindi, Bhojpuri, Maithili, and Urdu.
Industrial Profile
Araria is one of the backward districts in Bihar and is receiving funds from the Backward Regions Grant Fund Program. There are a large number of artisan workers in the district, and bamboo cultivation is in plenty. Bamboo-based handicraft industries can be promoted through skill generation and training.
The major industries in the district include jute and plywood industry, with potential for agro-based industries. There is also good potential for the hotel industry and tourism-related enterprises due to its historical importance.
Infrastructure
The largest industrial belt of the district is Forbesganj, with a total of 309 hospitals and health centers. There are 90 commercial banks and financial products in the district. The district has a total of 552 primary schools, 162 middle schools, 18 secondary and senior secondary schools, and four colleges.
Some of the schools in Araria include Scottish Public School, Araria Public School, Career Academy, Girls’ Ideal Academy, and others.
- Transportation Network: Araria’s transportation network is developing. Roads are the primary mode of transportation within the district. National Highway 27 connects Araria to other major towns and cities. Limited railway connectivity exists.
- Healthcare Facilities: Araria’s healthcare infrastructure is also developing. There are government hospitals and primary health centers spread across the district. However, access to advanced medical facilities may be limited.
- Educational Institutions: Educational institutions such as government schools and colleges are present in Araria. The literacy rate is improving, but there is still scope for further development in the educational sector.
Heritage & Tourism
Araria has several notable attractions, such as Madanpur, Palasi, and Basaithi. It shares its northern border with Nepal and is the natural habitat of the Gangetic Dolphins, scientifically known as Platanista Gangetica.
Additionally, Araria is home to various famous temples, including Kali Mandir Temple. There is a Replica Stoop near Manikpur. It is located 5 km from the district headquarters when heading towards Forbesganj.
Geography & Climate
Araria district covers an area of approximately 2,830 square kilometers. Araria is known for its fertile agricultural land, with the Kosi River flowing through the region, providing water for irrigation. Araria District experiences a subtropical climate with hot summers and cool winters. The summer months, from March to June, are hot and dry, with temperatures often exceeding 40 degrees Celsius.
Monsoon season arrives in July and lasts until September, bringing heavy rainfall to the region. Winters, from November to February, are cool and pleasant, with temperatures dropping to around 10 degrees Celsius.
Economy & Industries
The primary occupation in the Araria district is agriculture. A significant portion of the district’s residents rely on farming for their livelihood.
Agriculture
- Dominant Crops: Paddy (rice) is the main cash crop cultivated in Araria. Maize (corn) and jute are also grown in abundance.
- Irrigation Methods: While specific data on irrigation methods in Araria is limited, typical methods used in Bihar include canals, wells, and tube wells.
Currently, Araria does not have a large industrial sector. The district is classified as one of India’s most backward districts and is working towards development initiatives.
Culture & Places of Interest
Araria district showcases a rich cultural legacy. The primary language spoken is Magadhi (a dialect of Hindi), while Bengali and Urdu are also used. The community celebrates prominent Hindu festivals like Chhath Puja, Durga Puja, and Holi with fervor, and Eid and Muharram hold significance for the Muslim population.
While Araria may not be a major tourist destination, it offers some great places to visit:
- Historical Significance: Araria’s history is linked to the ancient Mithila Kingdom. A replica stupa (Buddhist monument) near Manikpur serves as a reminder of the region’s historical past.
- Religious Sites: Several temples and mosques showcase Araria’s religious diversity. The six-story Kali Mandir and the Shiva Mandir in the heart of Araria city are significant Hindu pilgrimage sites. The Jama Masjid and Quba Masjid cater to the Muslim community.
- Natural Beauty: The Raniganj Vriksh Vatika Park provides a peaceful escape with its lush greenery.
For more detailed information about Araria District, please refer to the PDF document provided below.
Download PDF Here: Download Now!
FAQs
How many blocks are in the Araria district?
Araria district is divided into 9 blocks, namely Araria, Jokihat, Kursakanta, Raniganj, Sikti, Palasi, Forbesganj, Narpatganj, and Bhargama.
What is the primary occupation in Araria District?
Agriculture is the primary occupation in Araria District, with a focus on crops like rice, maize, and jute.
Which key industries operate in Araria, and why are they significant?
Key industries in Araria include agriculture, textiles, retail, and education. They are significant for driving economic growth and employment opportunities in the region.
What are the major crops grown in Araria District?
The major crops grown in Araria are rice, maize, and jute, taking advantage of the fertile plains in the region.
How is the transportation network in Araria District?
Araria has a well-connected transportation network with roads, railways, and access to the East-West Corridor, facilitating easy movement within the district and to other parts of the country.
What facilities are available in Araria for healthcare and education?
Araria offers healthcare facilities and educational institutions to cater to the needs of its residents, with a growing focus on providing quality services in these sectors.